Certain ligating molecules can be used as selective extractants for lanthanides recovery (Rare Earth Elements,REEs). Marshallton Research Laboratories offers a tool box of extractants for the separation of actinides and lanthanides, and the purification of individual elements from within these groups. Chemically, the ligands fall in several main categories: diamides, phosphonates, diphosphonates. Listed below are the molecules from the synthetic portfolio which are attractive candidates for the sequestration of REEs through ore processing or recycling.
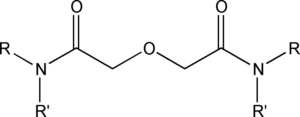
Diglycolamides (DGAs): e.g. TODGA, T2EHDGA, DMDODGA, TEDGA, DGA6
Diglycolamides (DGAs) were first developed for actinide/ lanthanide partitioning in the nuclear fuel cycle. a They are emerging as an effective alternative to organophosphorus acids (e.g. PC88A) for the separation of heavy REEs from light REEs.b DGAs operate without consuming large quantities of acids and bases, eliminating a secondary salt waste stream.c
-
-
- TODGA (R=R’=n-octyl)
- T2EHDGA R=R’=2-ethylhexyl)
- TEDGA (R=R’= ethyl)
- DMDODGA (R=methyl, R’=n-octyl)
- SDGA (R=3,5,5-trimethylhexyl, R’=n-octyl)
-
Next generation DGAs
Patent application US 2022/0002840 A1 (ORNL, INL) discloses a new class of DGAs with increased extraction and separation throughput of light REEs. DGA6 d US 17/366,172 is a superior product specifically designed to increase extraction and separation throughput of light REEs with markedly improved phase disengagement behavior. As a licensee, Marshallton Research Laboratories is making these advanced extractants available for REE applications.
a) Tachimoris, et al. Ion Exchange and Solvent Extraction; Vol. 19, pp 1 – 65 (2010)
b) Ellis, R.J. Inorganic Chemistry 2017, 56(3) 1152
c) Lee, M.-S. et al. Separation Purification Technology, 2005, 46(1), 72
d) Jansone-Popova,S. et al. US Patent Application, 17/366,172
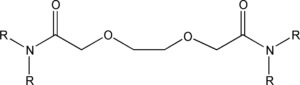
Dioxaoctanediamides (DOODAs) (e): e.g. DOODA(C1), DOODA(C2), DOODA (C8)
-
-
- DOODA(C1) (R=methyl)
- DOODA(C2) (R= ethyl)
- DOODA(C8) (R=n-octyl)
-
Diamides of this class facilitate separation of Am, Cm and lanthanides.
e) Sasaki, Y. et al. Solvent Extraction Research and Development, Japan Vol.18, 93-101 (2011)
2-Ethylhexyl-Bis(N,N’-di(2-ethylhexyl)acetamidoamine, ADAAM(EH)(f)
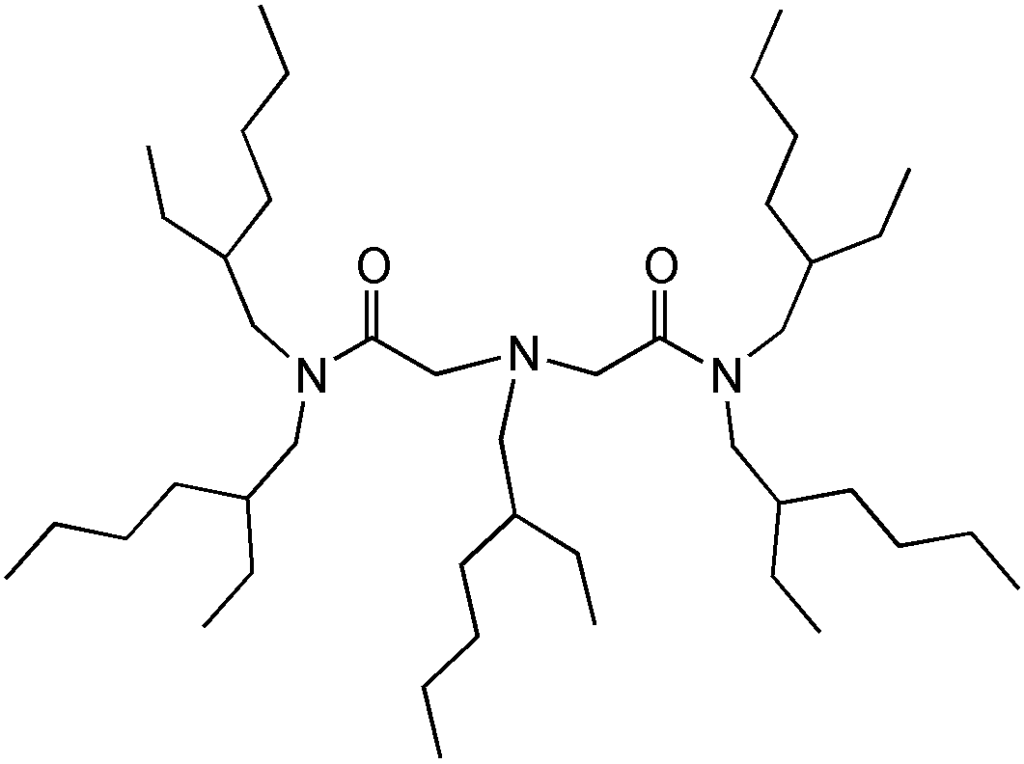
This aminodiamide ligand has been used in extraction of Am(III) and Eu(III) from nitric acid media.
f) H. Suzuki, et al. (2016) “Highly Practical and Simple Ligand for Separation of Am(III) and Eu(III) from Highly Acidic Media” Analytical Sciences 32: 477-479
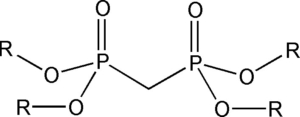
Organophosphous extractants(g-i): e.g. HEH[EHP], DBBP, TBMDP
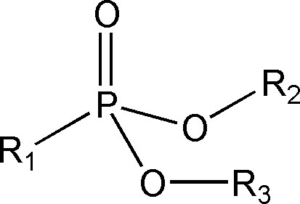
This class of ligands has been successfully used in separations of trivalent actinides from transuranic elements and separations of REEs.
-
-
- HEH[EHP] (R1=R2=2-ethylhexyl, R3=H)
- DBBP (R1=R2=R3=butyl)
- DAAP (R1=R2=R3= amyl)
-
-
-
- TBMDP (R=butyl)
- TAMDP (R=amyl)
-
Tetraalkyl methylene diphosphonate are excellent agents for extracting lanthanides and actinides.
g) D. Li (2019) “Development Course of Separating Rare Earth with Acid Phosphorus Extractants: A Critical Review”. Journal of Rare Earths, 37(5):468-486.
h) G.J.Lumetta (2010) “Review: Solvent Systems Combining Neutral & Acidic Extractants for Separating Trivalent Lanthanides from the Transuranic Elements” Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange 28(3): 287-312
i) Eliar, A. et al. (1996) Hydrometallurgy 40, 189-194